SpaceEye-T
EO
Planned
Satrec Initiative
Planned for launch in early 2024, SpaceEye-T is a commercial high resolution imaging satellite that will be owned and operated by the Korean satellite manufacturer Satrec Initiative (SI). SpaceEye-T will form the first component of SI’s plan to create a privately owned constellation of high resolution imaging satellites.
Quick facts
Overview
| Mission type | EO |
| Agency | Satrec Initiative |
| Mission status | Planned |

Summary
Mission Capabilities
SpaceEye-T will carry a single instrument, an electro-optical imager designed and developed by SI, known as EOS-T. The instrument is the latest in a series of very-high resolution optical imaging instruments produced by SI.
Performance Specifications
EOS-T will image in five bands, one panchromatic as well as four multispectral, and will provide a spatial resolution of 0.3 m in its panchromatic band and 1.2 m in its multispectral bands, with a swath width of 14 km.
SpaceEye-T is expected to have an orbit altitude of 600 km.
Space and Hardware Components
The SpaceEye-T satellite platform is expected to have a mass of approximately 700 kg. Its ground segment will be managed by two SI affiliates, Satrec Initiative Imaging Services (SIIS) and Satrec Initiative Analytics, who will commercialise SpaceEye-T data and products, as well as operating the satellite.
Overview
Satrec Initiative (SI) of Daejeon, South Korea, a satellite maker under South Korea’s Hanwha Group, will send a high-resolution imaging satellite called SpaceEye-T into low Earth orbit by the first quarter of 2024, in the first step toward building its own constellation of Earth observation satellites. 1)
The company unveiled the plan on August 18, 2021 saying SpaceEye-T will present its technological capabilities to potential civilian and military customers at home and abroad amid increasing demand for satellite-based Earth observation data.
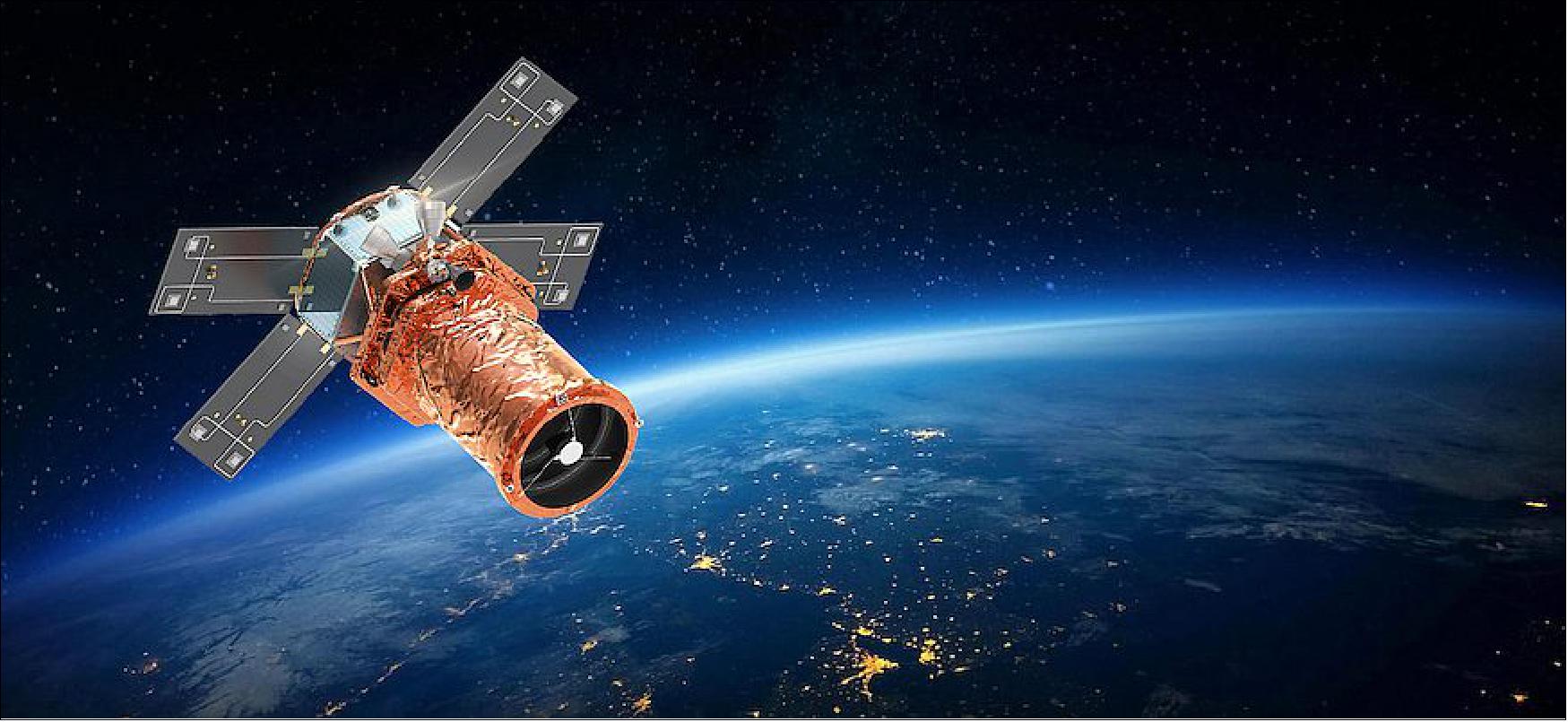

The 700 kg satellite is designed to offer a GSD (Ground Sample Distance) of 30 cm, with a swath width of 12 km, according to a news release. Satrec Initiative has not selected a launch vehicle for SpaceEye-T, which it aims to complete in 2023 for an undisclosed cost.
“We see an increasing demand for satellite-based Earth observation data, particularly in the fields of energy, climate monitoring, disaster management, and reconnaissance and surveillance for military purposes,” Jeon Bong-ki, a Satrec Initiative executive, told SpaceNews. “SpaceEye-T will pave the way for the company to enter these increasingly lucrative markets.”
He noted that the launch of SpaceEye-T would mark the beginning of the company’s journey toward building its own constellation of Earth observation satellites, but didn’t elaborate further.
He said while Satrec Initiative is responsible for developing SpaceEye-T, its two affiliates — SIIS (SI Imaging Services) and SIA (SI Analytics) — will be committed to operating the satellite and commercialising its collected data.
Satrec Initiative is South Korea satellite maker founded in 1999 by the engineers who developed the first Korean satellite (KITSAT-1) at KAIST Satellite Technology Research Center. It became an affiliate of South Korea’s conglomerate Hanwha Group in January after the group’s defence business arm, Hanwha Aerospace, purchased a 30% stake in Satrec Initiative for about $100 million.
SpaceEye-T is planned to have a mission lifetime of five years, with the potential to extend this to seven years. 1) 2) 7)
Spacecraft
The SpaceEye-T mission is expected to utilise a relatively small satellite bus, weighing approximately 650 kg. The bus design reflects the increasing miniaturisation of the existing bus design used in the SpaceEye-1 mission, and has improved agility and geolocation accuracy. Spacecraft agility has been improved by a factor of two, through the introduction of high-torque reaction wheels, allowing manoeuvre capability of 15.4 seconds from 200 km ground retargeting and ±45° roll, ±30° pitch tilting capabilities. Geolocation accuracy has also been improved by a factor three, through the use of enhanced attitude sensors and control algorithms. The SpaceEye-T bus has an image transmission rate of 1.6 Gbps, with dual polarisation. 1) 4)
Launch
SpaceEye-T is planned for launch in early 2024 5)
Mission Status
- January 14, 2021: Hanwha Aerospace, South Korea’s largest defence company, announced plans Jan. 14 to invest approximately $100 million to purchase 30% of the shares of satellite manufacturer Satrec Initiative.
- August 18, 2021: Satrec Initiative announced its high-resolution SpaceEye-T mission, planned for launch in early 2024 5)
Sensor Complement
SpaceEye-T will carry SI’s electro-optical imaging instrument, EOS-X, a successor to the EOS-T imager shown in Figure 2. SI has said the instrument will image in five bands, one panchromatic band and four multispectral bands. EOS-X will provide a spatial resolution of 0.3 m in its panchromatic band, and a spatial resolution of 1.2 m in its multispectral bands at nadir, with a swath width of 14 km at an orbit altitude of 600 km. SpaceEye-T is planned to operate in five different imaging modes, strip imaging operations, multiple strip imaging operations, single pass multi-stereo imaging operations, single pass wide area imaging operations and arbitrary inclined strip imaging operations. These advanced operations are enabled by enhanced spacecraft agility and geolocation accuracy. 3)
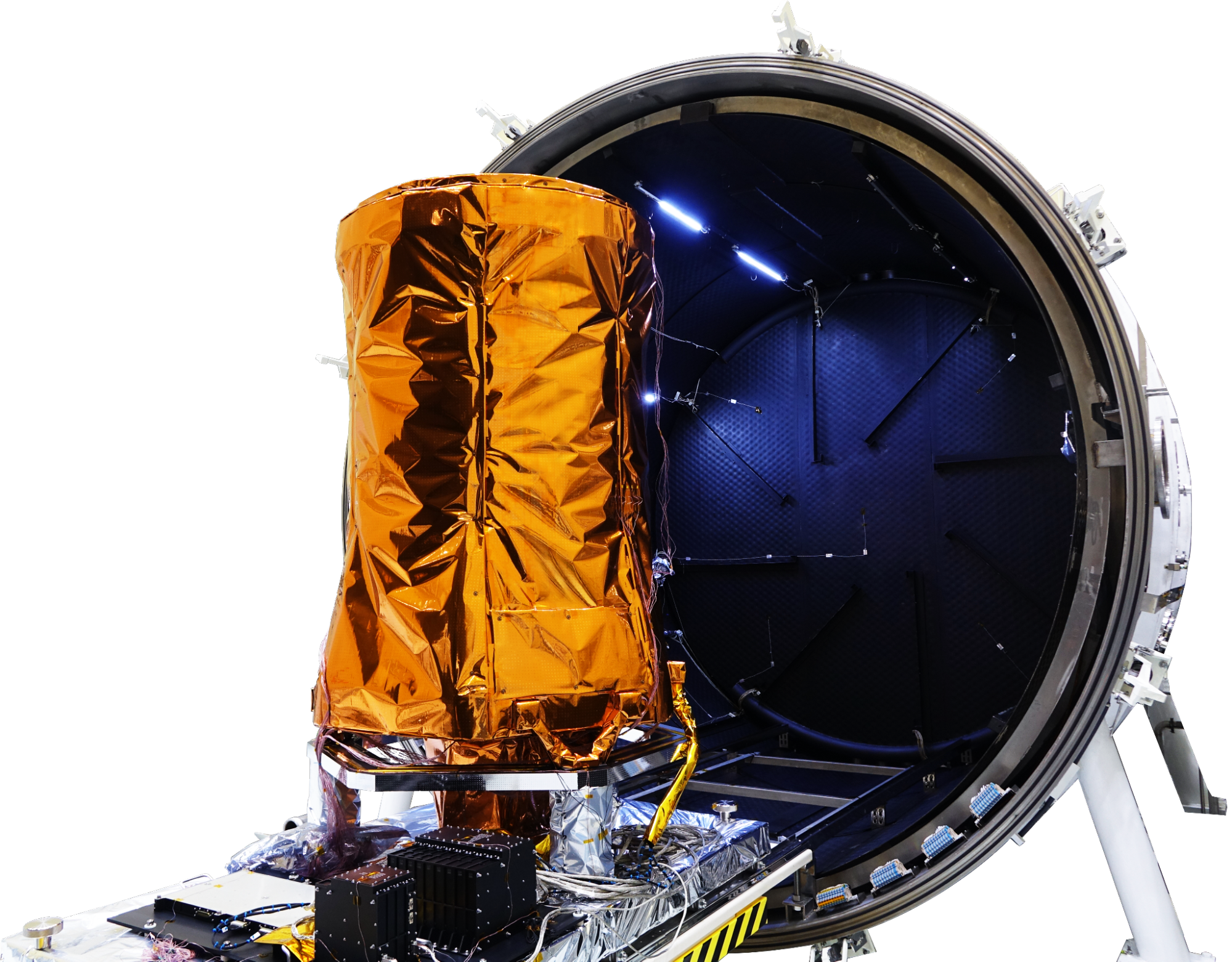
Ground Segment
The SpaceEye-T ground segment will be directly managed by its two affiliate companies, Satrec Initiative Imaging Services (SIIS), which is also the exclusive data provider for the Korean Multipurpose Satellite (KOMPSAT) series, and Satrec Initiative Analysis (SIA), which provides AI-native geospatial intelligence solutions for satellite imagery. These affiliates will operate the satellite and will be charged with commercialising its data and products. 2) 6)
References
1) “Electro-Optical Payloads – 쎄트렉아이.” Satrec Initiative, https://www.satreci.com/sub0102 Accessed 6 March 2023.
2) “Ground Systems – 쎄트렉아이.” Satrec Initiative,https://www.satreci.com/sub0103 Accessed 6 March 2023.
3) Lee, Hungu, et al. “Performing Earth Observation Missions Using Micro and Small Satellites.” Asia Pacific International Symposium on Aerospace Technology, 5 December 2019, URL: https://www.satreci.com/sub0404/file_down/id/456
4) “Satellite Systems – 쎄트렉아이.” Satrec Initiative, https://www.satreci.com/sub0101 Accessed 6 March 2023.
5) “Satrec Initiative aims to build world's highest-resolution optical satellite.” The Korea Herald, 18 August 2021, https://www.koreaherald.com/view.php?ud=20210818000790. Accessed 6 March 2023.
6) “South Korea's Satrec Initiative to build constellation of high-resolution Earth observation satellites.” SpaceNews, 18 August 2021, https://spacenews.com/south-koreas-satrec-initiative-to-build-constellation-of-high-resolution-earth-observation-satellites/. Accessed 6 March 2023.
7) “Suppliers » Satrec Initiative.” Skybrokers,https://sky-brokers.com/supplier/satrec-initiative/. Accessed 6 March 2023.