Starlette / Stella
EO
CNES
Gravity and Magnetic Fields
Gravity, Magnetic and Geodynamic measurements
Launched in February 1975 and September 1993 respectively, STARLETTE (Adapted Size Satellite with Laser Reflectors for Earth Studies) and Stella are near identical satellites operated by France’s Space Centre, CNES. Their Low Earth Orbit (LEO) is sensitive to Earth’s gravitational field which is affected by changes in oceanic tides and the Earth’s structure. It is these two contributing factors to Earth’s gravitational field that the satellites are studying.
Quick facts
Overview
| Mission type | EO |
| Agency | CNES |
| Mission status | Operational (nominal) |
| Launch date | 06 Feb 1975 |
| Measurement domain | Gravity and Magnetic Fields |
| Measurement category | Gravity, Magnetic and Geodynamic measurements |
| Measurement detailed | Gravity field |
| Instruments | Laser Reflectors |
| Instrument type | Precision orbit |
| CEOS EO Handbook | See Starlette / Stella summary |

Summary
Mission Capabilities
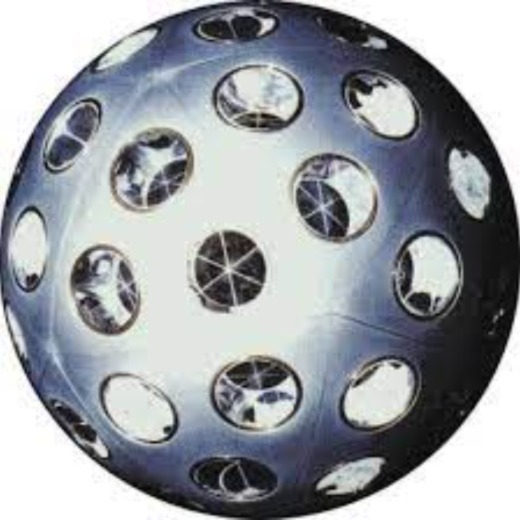
STARLETTE and Stella each carry 60 retroreflectors, which reflect back lasers sent by Satellite Laser Ranging (SLR) ground stations to pinpoint the orbit of the satellite. The small mass of both STARLETTE and Stella (47.29 kg and 48 kg respectively) means that their orbits are influenced by slight changes in Earth’s gravitational fields and these small adjustments to their orbits can be detected by the more than 40 SLR sites around the globe. The causes of the slight gravitational changes, oceanic tides and Earth's structure, is what STARLETTE and Stella aim to study.
Performance Specifications
Starlette undertakes a non-sun-synchronous orbit with an altitude of 812 km, an inclination of 49.83°, and a period of 104 minutes. Stella also undertakes a non-sun-synchronous orbit but with an altitude of 800 km, an inclination of 98.6°, and a period of 101 minutes.
Space and Hardware Components
STARLETTE and Stella were launched from the Kourou launch site in French Guiana onboard a Diamant BP4 launch vehicle and an Ariane 4 launch vehicle respectively.
Due to the small mass of STARLETTE and Stella, they are expected to operate up until at least 2050.
Starlette / Stella - Geodetic Satellites
Starlette (Satellite de Taille Adaptée avec Réflecteurs Laser pour les Etudes de la Terre) is a `Solid Earth' mission of CNES (Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales), France, a passive satellite dedicated to geodetic and geophysical studies with SLR (Satellite Laser Ranging) observation support. Starlette is the world's first passive laser satellite for solid Earth research covered with 60 laser retroreflectors.
Objectives: SLR tracking data is used to study the long wavelength gravity field and its temporal change along with determining the frequency dependent tidal responses of the solid earth and to improve the knowledge of the long wavelengths of the ocean tides. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5)
Spacecraft
Starlette and Stella are virtually identical French passive satellites launched by CNES in 1975 and 1993, respectively. Their small size compared to their mass gives them a much larger sensitivity to the gravitational attraction than to the surface forces due either to the residual atmosphere at the satellite or to radiation pressure.
Launch
Launch: The Starlette spacecraft was launched on Feb. 6, 1975 from Kourou on a Diamant BP4 launch vehicle (representing the first Diamant BP4 flight).
Launch: The Stella spacecraft was launched on Sept. 26, 1993 from Kourou. Stella was put on top of Ariane's 3rd stage with a special device, including a spring to give the required increment of velocity and a spin of 5 to 8 rev/minutes (spin axis perpendicular to the ecliptic). Stella was a secondary payload to the SPOT-3 spacecraft of CNES..
Parameter | Starlette | Stella |
Launch date | Feb. 6, 1975 from Kourou | Sept. 26, 1993 from Kourou |
COSPAR ID | 7501001 | 9306102 |
RRA (Retro¿Reflector Array) diameter | 24 cm | 24 cm |
Satellite shape | sphere | sphere |
RRA reflectors | 60 corner cubes | 60 corner cubes |
Satellite mass | 47.29 kg | 48 kg |
Satellite orbit | Perigee=812 km, eccentricity=0.0206, inclination= 49.83º, period=104 minutes | Perigee=800 km, eccentricity= 0.0206, inclination=98.6º, period=101 minutes |
Life expectancy | Many decades | Many decades |
Orbit: The orbital altitudes of Starlette and Stella were selected so as to be long-term but also sensitive to gravity field and its temporal variations and even to the solid Earth and ocean tides.
• Starlette near-circular orbit: altitude of 812 km, inclination = 49.83º (providing geodetic coverage up to the mid-latitudes), period=104 minutes.
• Stella was launched into a polar orbit to provide geodetic coverage of the polar regions missed by Starlette. Stella orbit: mean altitude = 800 km, inclination = 98.6º, period = 101 minutes.
Measurement campaigns required the support of the worldwide SLR network. However, at the time of Starlette's launch, the so-called laser network of ground stations was in its very early stage - it took some time to get better measurement techniques installed and operating.
As expected, Starlette was also sensitive to the tidal potential and allowed researchers to determine the tidal potential parameters. Despite the limitations in coverage due to weather conditions and anisotropy of the laser network, the laser technique continued to be used and was upgraded again and again. 6)
Mission Status
• In 2012, both satellites are in orbit and are being tracked from time to time by the SLR network. The life expectancy for SLR tracking is considered to be possible over many decades.
• SLR Center of Mass Offset for Starlette & Stella 7) 8)
• In the words of Francois Barrier and Michel Lefebvre (the authors of reference 5): “In the early stages of satellite laser tracking (1973) it was difficult to explain to management that Starlette was a “passive” satellite (no telemetry was foreseen) --- but we expect to track it for decades if not for centuries to study the “dynamics” of the Earth. Starlette is not alone, the sister satellite Stella was launched as a passenger of SPOT-3 in 1993.”
References
1) M. Lefebvre, “Stella,”, CSTG, `New Satellite Missions for Solid Earth Studies-Status and Preparations,' CSTG Bulletin No. 11, 1989, pp. 25-32
2) J. G. Marsh, R. G. Williamson, “Precision orbit computations for Starlette,” Journal of Geodesy, Vol. 52, No 1, March 1978, pp. 71-83
3) http://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/satellite_missions/list_of_satellites/star_general.html
4) Ramesh Govind, “Determination of the Temporal Variations of the Earth's Centre of Mass from Multi-Year SLR Data,” 15th International Laser Ranging Workshop, Oct. 15-20, 2006, Canberra, Australia, URL: http://cddis.gsfc.nasa.gov/lw15/docs/presents/Monday1630.pdf
5) F. Barlier, M. Lefebvre, “A new look at planet Earth: Satellite geodesy and geosciences,” The Century of Space Science, 2001, pp. 1623-1651, Kluwer Academic Publishers, URL: http://www.ipgp.jussieu.fr/~tarantola/Files/Professional/Teaching/Seminar/Texts/Barlier-Lefebvre.pdf
6) M. K. Cheng, C. K. Shum, R. J. Eanes, B. E. Schutz, B. D. Tapley, ”Observed temporal variations in the Earth's gravity field from 16-years of Starlette orbit analysis”, Proceedings of the XX General Assembly of the IUGG, IAG Symposium No. 3, Vienna, Austria, August 1991
7) “SLR Center of Mass Offset for Starlette & Stella, Effect of Range Biases on Geocenter Estimation,” GGOS Working Group on Ground Networks and Communications Working Group Meeting, Vienna, Austria, April 16, 2008, URL: http://192.106.234.28/Components/BNC/GNC/GNC%20Meeting%20Apr%202008/SLR%20bias%20CoM%
20offset%20issues%20impact%20on%20the%20TRF%20scale.pdf
8) P. Lejba, S. A. Schillak, E. Wnuk, “Determination of orbits and SLR stations' coordinates on the basis of laser observations of the satellites Starlette and Stella,” Advances in Space Research, Vol. 40, Issue 1, 2007, pp. 143-149
The information compiled and edited in this article was provided by Herbert J. Kramer from his documentation of: ”Observation of the Earth and Its Environment: Survey of Missions and Sensors” (Springer Verlag) as well as many other sources after the publication of the 4th edition in 2002. - Comments and corrections to this article are always welcome for further updates.